You can use Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) as a Policy Information Point (PIP) Data Source in the PlainID Authorization Platform. This setup allows you to pull user and group data directly from Entra ID into the Platform’s policy evaluation flow.
Note: The Microsoft Entra ID connector is currently supported only with Identity Templates.
Refer to the User Property Table for a detailed breakdown of available attributes and capabilities.
Creating a Microsoft Entra ID Data Source
-
In either the Environment Settings or Tenant Settings screen, open the PIP Settings tab.
-
From the Policy Authorization Agent dropdown, select the PAA where you'd like to configure the new Data Source.
-
Click New Data Source.
-
Provide a unique name for your Data Source.
-
Under Connection Adapter, select Azure Active Directory.
-
In the Connection Settings section:
- Select your Policy Authorization Agent from the dropdown.
- Enter the Microsoft Graph API endpoint:
https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0 - Follow the OAuth configuration instructions:
-
If using OAuth Authentication with your Data Source, modify the following inputs in the Policy Authorization Agent section(s):
-
Under the Security Type field, choose None.
-
In the Translator Properties section, add the following properties with these key-value pairs:
- Key = authConf, Value = "<path of the
auth-config.xmlfile as described in OAuth2 Authentication Support.>" - Key = securityDomain, Value = "<name of the
application-policyin your service's XML file.>"
- Key = authConf, Value = "<path of the
-
Note: Ensure that all PAAs in each group share the same XML file.
Click here for more information about setting up OAuth for your Data Sources.
-
-
Click Test Connection to validate network communication between the PAA and Microsoft Entra ID.
Note: This test only checks connectivity. It does not validate Entra ID credentials at this stage.
-
Under the Models section, enter a unique name for the virtual schema.
-
In the DDL field, define a valid DDL to fetch Microsoft Entra attributes. See Valid DDLs for examples and syntax.
-
Click Create to finalize the Data Source configuration.
Valid DDLs
Default Usage
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE Users (
id string NOT NULL,
displayName string UNIQUE,
userPrincipalName string NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_USERS PRIMARY KEY(id)
) OPTIONS (
UPDATABLE TRUE,
nameinsource 'Users',
"teiid_odata:EntityType" 'users',
"teiid_odata:Type" 'ENTITY_COLLECTION'
);
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE UserGroups (
displayName string UNIQUE,
userID string OPTIONS (
UPDATABLE FALSE,
"teiid_odata:PSEUDO" 'true'
),
id string,
FOREIGN KEY(userID) REFERENCES Users (id),
CONSTRAINT PK_USERRS_GROUPS PRIMARY KEY(userID, id)
) OPTIONS (
NAMEINSOURCE 'memberOf',
UPDATABLE TRUE,
"teiid_odata:NameInSchema" 'memberOf',
"teiid_odata:Type" 'NAVIGATION_COLLECTION'
);
Note: This is the recommended schema for most use cases. Avoid using the "Generate DDL" option for the Entra ID connector.
Custom Attributes
You can fetch custom or nested attributes from Entra ID using JSONPath. Use the plainid:inner-attribute-jsonpath option, with plainid:parser to define how the inner attribute should be handled.
onPremisesExtensionAttributes string options (
"plainid:inner-attribute-jsonpath" '$.extensionAttribute1',
"plainid:parser" 'jsonpath'
)
Full Example:
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE Users (
id string NOT NULL,
onPremisesExtensionAttributes string options (
"plainid:inner-attribute-jsonpath" '$.extensionAttribute1',
"plainid:parser" 'jsonpath'
),
displayName string UNIQUE,
userPrincipalName string NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_USERS PRIMARY KEY(id)
) OPTIONS (
UPDATABLE TRUE,
nameinsource 'Users',
"teiid_odata:EntityType" 'users',
"teiid_odata:Type" 'ENTITY_COLLECTION'
);
Translator Properties
You can optionally configure translator properties for more control over how data is fetched. These properties allow customization such as filtering, paging, multithreading, and fetching nested group relationships.
Check out our Translator and Model Properties article for more information about Translator Properties.
For advanced filtering, performance tuning, and other use cases, refer to the sections below.
Fetching User Properties
PlainID supports several translator properties to control how user and group data is fetched from Entra ID:
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
enableNestedMemberOf |
false |
Enables fetching of transitive (nested) group memberships. |
includeGroupsList |
— | List of group names to include in the fetch. |
excludeGroupsList |
— | List of group names to exclude from the fetch. |
enableGroupFirstMemberOf |
false |
Improves caching performance by fetching groups first, then members. |
graphApiFilterToAppend |
— | Adds a native Graph API filter to the group query. |
defaultPageSize |
999 |
Number of items per page in Graph API responses. |
useExpandMemberOf |
false |
Uses Graph API’s expand to fetch group memberships more efficiently. |
maxWorkers |
1 |
Number of threads used to parallelize group fetching. |
Fetching Nested Groups
Set enableNestedMemberOf=true to use the transitiveMemberOf Graph API endpoint and fetch hierarchical group memberships.
⚠️ This option only works for single-user queries when
enableGroupFirstMemberOf=false.
Filtering Groups
You can filter group data in several ways:
1. Object Attribute Filtering
- Add a
WHEREclause in the View definition. - Use
graphApiFilterToAppendfor native Graph API filters, e.g.:
startswith(displayName,'HR')orgroupTypes/any(c:c eq 'Unified')
⚠️ Not all SQL
WHEREclauses translate successfully to Graph API.
2. Include/Exclude Lists
- Use
includeGroupsListorexcludeGroupsListto define group subsets. - Lists must be comma-separated with no spaces.
Page Size
Adjust the defaultPageSize property to control how many results are fetched per Graph API request (up to 999). This can significantly impact performance with large datasets.
Using Expand MemberOf
Set useExpandMemberOf=true to use Graph API's $expand=memberOf, which is efficient if most users belong to fewer than 20 groups.
⚠️ If
enableGroupFirstMemberOf=true, you must setuseExpandMemberOf=false.
Fetching Users Using Parallel Threads
Use the maxWorkers property to enable multithreading for group data fetching. This improves performance on large Entra ID environments. Adjust based on your environment and performance goals.
Redis-Based Request Distributed Caching
The Redis-based Request Distributed Cache feature optimizes data retrieval for REST and Entra ID translators by introducing a shared caching mechanism between PIP instances.
This feature significantly reduces redundant data service calls and improves performance, especially when working with large data sets or when full data sets are fetched into the PIP cache.
Ensure that you use this feature solely with a PIP Caching Materialized View. For more information, refer to Caching Views.
When multiple PIP instances request the same data from a source, such as Entra ID, the caching mechanism ensures that:
- Only one PIP instance sends the data request to the source.
- This instance stores the response in a shared Redis cache as a distribution location.
- All other PIP instances retrieve the cached response directly from Redis instead of making new requests to the external service.
This process reduces load on the data source, minimizes redundant network calls, and improves overall efficiency when loading large data sets into PIP Cache.
Enabling Redis caching requires additional Redis resources for the duration of data distribution to all PIP instances.
Before enabling, consult with Professional Services to evaluate the appropriate Redis capacity based on your data set size and data source characteristics.
Configuration
To enable this feature, set the following translator property:
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
redisCacheEnabled |
Enables the Redis caching mechanism. | false |
Once enabled, you can fine-tune cache behavior using the following property:
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
valueTtlMs |
Defines how long cached values are retained in Redis (in milliseconds) available for distribution to PIP instances. Higher values retain data longer but increase cache memory usage for a longer duration. | 300000 |
Example Scenario
Three PIP instances (PIP1, PIP2, and PIP3) in a PAA are deployed in the same cluster, configured to use Redis caching.
Each instance processes identical data requests, such as fetching a User Materialized View from the Data Source
Without Redis caching, all three PIPs would independently query the Data Source, creating unnecessary load and duplication.
With Redis-Based Requests Distributed Cache enabled:
- PIP1 sends the initial data request to the Data Source.
- PIP1 stores the retrieved data in the Redis cache and loads it into its local memory.
- When PIP2 and PIP3 issue the same request, they find the response already cached in Redis.
- Instead of re-querying Azure, PIP2 and PIP3 pull the data directly from Redis.
As a result:
- The data source (like Entra ID or REST) receive only one request (per page).
- All PIP instances share the same consistent data.
- Overall system performance improves, particularly for large data sets or high-frequency REST calls.
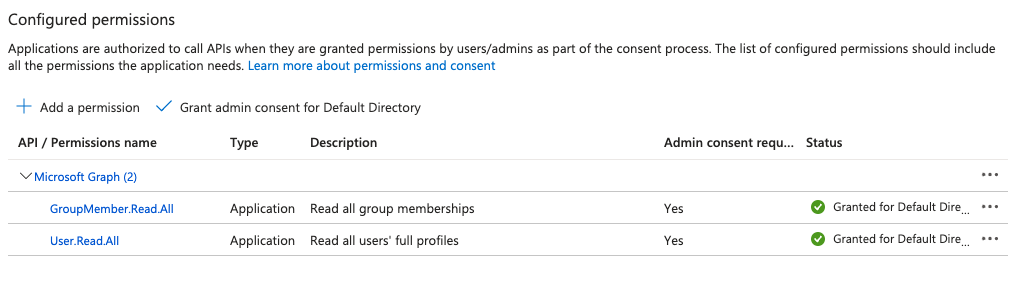
Required Microsoft Entra Permissions
Ensure your app registration in Microsoft Entra ID has the following Microsoft Graph API permissions:
GroupMember.Read.AllUser.Read.All
You can find these settings under API Permissions in the Azure portal:
Need help? Contact PlainID Support.