To connect to an external database via JDBC, you need to create a new JDBC-based Data Source in the Platform. This involves selecting the connector, configuring connection settings, defining a virtual schema (model), and optionally generating DDL statements. Follow the steps below to complete the setup.
Creating a JDBC Data Source
-
In the Tenant Settings screen, go to the PIP Settings tab.
-
From the Policy Authorization Agent dropdown, select the PAA where the new Data Source should be created.
-
Click New Data Source.
-
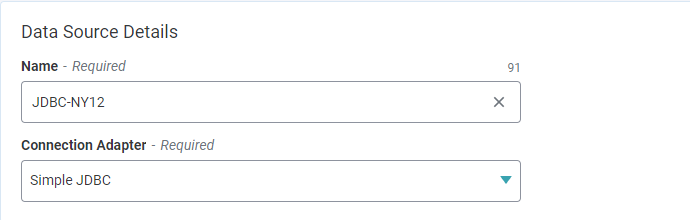
Enter a unique Name for the Data Source.
-
Under Connection Adapter, select the appropriate JDBC connector.
-
Fill in the Connection Settings, including:
- Driver Class Name
- JDBC URL
- Username (and any other required credentials)
-
Click Test Connection and provide a valid validation query based on the selected database.
Defining the Data Model
-
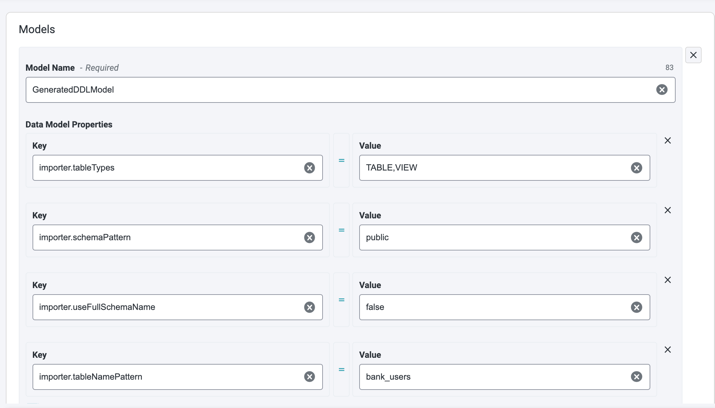
In the Models section, enter a unique Model Name.
-
Under Data Model Properties, add key-value pairs prefixed with
importer.to control how database objects are imported into the model.Common Importer Properties:
Parameter Description Default catalog Name of the catalog to fetch data objects from. null schemaPattern Exact schema name or wildcard pattern. null tableNamePattern Exact table name or wildcard pattern. null tableTypes Comma-separated list of table types (e.g., "TABLE","VIEW").excludeTables Regex to exclude specific tables. Supports negative look-ahead patterns. importKeys Whether to import primary and foreign key definitions. true importIndexes Whether to import index and cardinality metadata. false For more options, refer to: Data Model Properties for JDBC
Generating and Using DDL
-
Click Generate DDL to create a DDL statement based on the importer properties you defined.
-
The generated DDL appears in the DDL field.
-
Review and edit the DDL if necessary.
⚠️ Regenerating the DDL will overwrite any manual changes.
-
Alternatively, you can manually enter a custom DDL statement in the field.
Examples and Notes:
-
Use
schemaPatternortableNamePatternto limit DDL generation to specific schemas or tables. -
Oracle: Use the default schema name in the DDL.
-
MSSQL and others: Use
nameinsourceto specify schema-qualified table names, for example:CREATE FOREIGN TABLE my_table ( col1 string, col2 string ) OPTIONS (nameinsource 'schema123.table_name');
Visual Example:
-
Importer properties set:
-
Generated DDL:

-
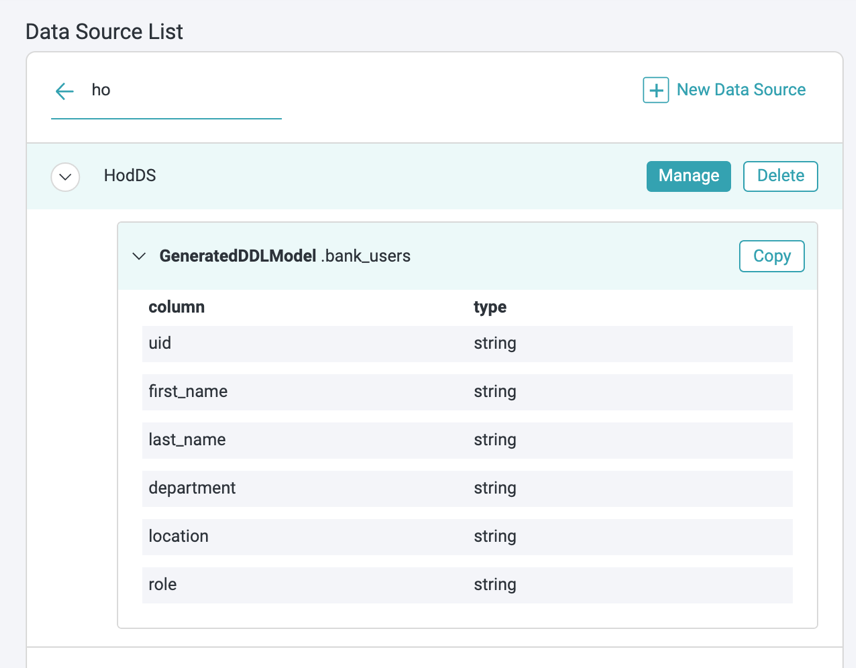
Model after saving:
Optional: Setting Translator Properties
- Click Set to define additional Translator Properties (only if needed).
- Enter each Key and Value pair.
Note: These settings are optional. For advanced usage, see Available Translator Properties for JDBC
- Click Save to complete the Data Source configuration.
Supported JDBC Translators
The following JDBC connectors are supported:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- DB2
- JDBC Simple
- Sybase
- Google BigQuery